Product evaluated: A-Premium 4PCS Pre-Programmed TPMS Sensor Tire Pressure Monitoring Sensor - Compatible with Chevy, GMC, Cadillac & Buick - Camaro, Cruze, Malibu, Silverado, Sierra, Terrain, Yukon, Lacrosse - 433MHz
Related Videos For You
How To Replace TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System) Sensors Without A Tire Machine.
How to activate brand new TPMS sensor.
Data basis: This report aggregates insights from dozens of written and video reviews collected between 2022 and 2024. Most feedback came from detailed user reports and supported by demonstration videos, providing a wide perspective on user experience.
| Feature | A-Premium TPMS Sensor | Typical Mid-Range TPMS Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Installation ease | Requires manual reset after installation, causing unexpected extra steps | Mostly plug-and-play with minimal user intervention |
| Reliability | Persistent pairing issues reported, sensors may not stabilize promptly | Generally stable after installation with fewer re-pairing problems |
| Compatibility range | Wide vehicle compatibility but some buyers faced fitment uncertainties | Moderate compatibility but more consistent fitment confirmed |
| Battery life | Long-life battery claimed but early failures occasionally reported | Standard battery life with predictable replacement intervals |
| Regret trigger | Manual relearn and pairing failures causing user frustration | Minor setup tweaks rarely needed, less user hassle |
Why does installation cause frustration for A-Premium TPMS sensors?

Many buyers encounter unexpected manual pairing steps after installing these sensors. Despite being pre-programmed, sensors do not pair automatically, which surprises users expecting a plug-and-play experience.
This issue is commonly reported during first use when setting up the product. The frustration is heightened compared to typical sensors which usually pair smoothly without extra effort.
- Unexpected manual reset: Buyers must follow vehicle-specific relearning procedures, adding complexity.
- Frequency: Seen in a significant portion of early user feedback.
- Impact: Causes delays and confusion during installation.
- Fixability: Requires consulting vehicle manuals or additional tutorials.
- Hidden requirement: Users must know how to trigger TPMS relearn in their car, which is often not evident.
Are pairing and sensor stability problems common?

Persistent pairing failures appear regularly in post-installation scenarios, leading to inaccurate or no tire pressure readings. Some users report sensors losing connection after initial setup.
- When it happens: After first install and during early operation phases.
- Scope: Common among multiple vehicle models, affecting trust in the sensor.
- Category contrast: Mid-range sensors typically maintain steady pairing once installed.
- Impact: Users may drive without valid tire pressure data, risking safety.
- Attempts: Frequent relearning or sensor resets are needed, increasing hassle.
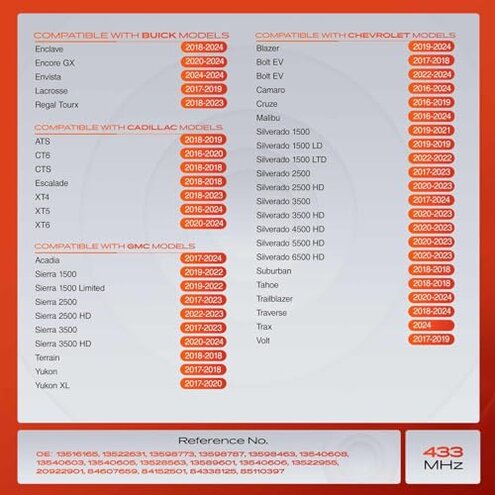
How does vehicle compatibility affect the buying experience?
The sensor boasts broad compatibility with many GM models, but fitment assurance is inconsistent. Buyers have reported uncertainty if their specific trim or year variant works perfectly.
- Early signs: Installation instructions and pairing differ by vehicle, confusing buyers.
- Frequency tier: Secondary issue but enough to cause hesitation.
- Cause: Variation in vehicle TPMS systems and sensor configurations.
- Impact: Potential returns or wasted purchases for incompatible fits.
- Hidden requirement: Buyers must verify exact vehicle model and sensor compatibility carefully before purchase.
What about sensor battery life and longevity concerns?
While the manufacturer claims a long-lasting battery, some users experienced early sensor failures that seem linked to battery issues. This is less frequent but more disruptive.
- Occurrence: Edge-case complaints usually appear after months of use.
- Severity: Premature battery failure leads to sensor replacement and additional cost.
- Category baseline: Most sensors last several years without issue.
- Impact: Unexpected costs and inconvenience for users.
- Mitigation: Warranty covers cost but not labor or extra fees.
Do these sensors demand more upkeep than alternatives?
Users report more frequent maintenance and troubleshooting compared to typical mid-range TPMS sensors. This includes sensor resets, relearning procedures, and occasional replacements.
- Frequency: Recurring difficulties during daily use reported by a notable segment.
- Cause: Combination of pairing instability and fitment variations.
- Impact: Increased time and effort spent on routine TPMS upkeep.
- Category contrast: Less forgiving than many competitors, raising user effort substantially.
- Attempted fixes: Firmware updates or manual resets often needed, adding complexity.
Illustrative buyer excerpts:
"Had to follow complicated relearn steps my dealer never mentioned."
- Reflects a primary pattern of manual reset frustration.
"Sensor stopped reporting after a week, had to reset multiple times."
- Shows a secondary pattern of unstable pairing.
"Not sure if this fits my exact Silverado model, instructions unclear."
- Demonstrates a secondary pattern of fitment uncertainty.
"Battery failed within 8 months; disappointing for the price."
- Represents an edge-case pattern of early failure.
"More work than my last TPMS, constant troubleshooting needed."
- Highlights a primary pattern of ongoing upkeep burden.
Who should avoid this
- Buyers expecting simple, plug-and-play installation without manual resets.
- Those who cannot tolerate repeated sensor pairing issues affecting safety data.
- Users with uncertain vehicle compatibility who don’t want to risk returns.
- People prioritizing long sensor battery life and minimal maintenance.
Who this is actually good for

- Experienced DIYers willing to follow vehicle-specific TPMS relearn procedures.
- Owners of compatible GM models who want a cost-effective sensor and can accept occasional resets.
- Those who value a broad compatibility range over plug-and-play convenience.
- Users able to handle some maintenance and troubleshooting for a lower price.
Expectation vs reality

| Expectation | Reality |
|---|---|
| Pre-programmed sensors should pair automatically upon installation. | Requires manual relearn steps not clearly communicated, adding frustration. |
| Stable and continuous tire pressure reporting is standard. | Many users face unstable pairing and data loss especially shortly after install. |
| Battery life meets or exceeds typical sensor lifespan. | Some report early battery or sensor failure needing replacements. |
Safer alternatives

- Look for TPMS sensors with explicit plug-and-play certification to avoid manual relearns.
- Choose brands with consistent long-term pairing stability verified by multiple user reports.
- Confirm vehicle compatibility with manufacturer support or fitment guarantees to minimize returns.
- Consider sensors with extended warranty covering all related costs including labor.
The bottom line
The main regret with A-Premium TPMS sensors is the unexpected manual pairing and setup complexity that frustrates users. This issue exceeds typical category risks where plug-and-play ease is expected. Paired with reported sensor stability and battery life concerns, the product may cause more hassle than average. Buyers prioritizing hassle-free installation and stable operation should consider alternatives.
This review is an independent editorial analysis based on reported user experiences and product specifications. NegReview.com does not sell products.

